- Make Bootable Osx Usb On Linux
- Make Bootable Os X Usb
- Make Bootable Osx Usb
- Make Bootable Osx Usb Without Mac
- Make Bootable Usb Os X Catalina
- Make Bootable Osx Usb Windows
When OS X shipped on a DVD a good number of years ago, you always had the convenience of a bootable installer—an OS X installer that could be used to boot your Mac if its own drive was having problems. But to install or reinstall a recent version of OS X, you must either download a non-bootable installer from the Mac App Store or (via OS X’s invisible, bootable recovery partition) download 6GB of installer data from Apple’s servers during the installation process. In other words, you no longer have the same safety net or convenience.
But to install or reinstall a recent version of OS X, you must either download a non-bootable installer from the Mac App Store or (via OS X’s invisible, bootable recovery partition) download 6GB.
Because of this, I recommend creating your own bootable El Capitan (OS X 10.11) installer drive on an external hard drive or USB thumb drive. If you need to install El Capitan on multiple Macs, using a bootable installer drive is faster and more convenient than downloading or copying the entire installer to each computer. If you want to erase the drive on a Mac before installing El Capitan, or start over at any time, you can use a dedicated installer drive to boot that Mac, erase its drive, and then install the OS (and subsequently restore whatever data you need from your backups). And if your Mac is experiencing problems, a bootable installer drive makes a handy emergency disk.
(OS X Recovery lets you repair your drive and reinstall OS X, but to perform the latter task, you must wait—each time you use it—for the entire 6GB of installer data to download. At best, that’s a hassle; at worst, it’s hours of waiting before you can get started.)
Choose the source or ISO file that you wish to make a bootable of. We have already downloaded the Ubuntu ISO, so that’s what we select. Persistence is basically the amount of disk space that is reserved as non-volatile. So that you can use the USB bootable without installing the OS and any changes you make will be made to the. Rufus won't make a bootable USB compatible with Mac as it cannot interpret the boot loader (at least not in Mavericks and up). Fat32 can't handle the 5+GB Mavericks image either. Not say you didn't get an older version to work, however, just to keep others from wasting their time. Much like prior versions of Mac OS, you can easily create a bootable install drive for MacOS Mojave 10.14. These boot install drives allow for things like easily formatting a Mac to perform a clean install of macOS Mojave, installing macOS Mojave onto multiple Macs without them each having to download the installer, or even as a troubleshooting tool since it can be booted from by any.
As with previous versions of OS X, it’s not difficult to create a bootable installer drive, but it’s not obvious, either. I show you how, below.
Keep the installer safe
Like all recent versions of OS X, El Capitan is distributed through the Mac App Store: You download an installer app (called Install OS X El Capitan.app) to your Applications folder. In this respect, the OS X installer is just like any other app you buy from the Mac App Store. However, unlike any other app, if you run the OS X installer from that default location, the app deletes itself after it’s done installing OS X.
If you plan to use the OS X installer on other Macs, or—in this case—to create a bootable installer drive, be sure to copy the installer to another drive, or at least move it out of the Applications folder, before you use it to install the OS on your Mac. If you don’t, you’ll have to redownload the installer from the Mac App Store before you can use the instructions below.
Make Bootable Osx Usb On Linux
What you need
To create a bootable El Capitan installer drive, you need the El Capitan installer from the Mac App Store and a Mac-formatted drive that’s big enough to hold the installer and all its data. This can be a hard drive, a solid-state drive (SSD), a thumb drive, or a USB stick—an 8GB thumb drive is perfect. Your drive must be formatted as a Mac OS Extended (Journaled) volume with a GUID Partition Table. (Follow this tutorial to properly format the drive if you’re using OS X Yosemite or older. If you’re using OS X El Capitan, use these instructions.)
Your OS X user account must also have administrator privileges.
Apple’s gift: createinstallmedia
In my articles on creating a bootable installer drive for older versions of OS X, I provided three, or even four, different ways to perform the procedure, depending on which version of OS X you were running, your comfort level with Terminal, and other factors. That approach made sense in the past, but a number of the reasons for it no longer apply, so this year I’m limiting the instructions to a single method: using OS X’s own createinstallmedia tool.
Starting with Mavericks, the OS X installer hosts a hidden Unix program called createinstallmedia specifically for creating a bootable installer drive. Using it requires the use of Terminal, but createinstallmedia works well, it’s official, and performing the procedure requires little more than copying and pasting.
The only real drawback to createinstallmedia is that it doesn’t work under OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard—it requires OS X 10.7 Lion or later. Though it’s true that some Macs still running Snow Leopard can upgrade to El Capitan, I think it’s safe to assume that most people installing OS X 10.11 will have access to a Mac running 10.7 or later.
(If you absolutely refuse to go near Terminal, an El Capitan-compatible version of DiskMaker X is now available, although I haven’t yet had the chance to test it.)
Make Bootable Os X Usb
Making the installer drive
- Connect to your Mac a properly formatted 8GB (or larger) drive, and rename the drive
Untitled. (The Terminal commands I provide here assume that the drive is named Untitled. If the drive isn’t named Untitled, the procedure won’t work.) - Make sure the El Capitan installer (or at least a copy of it), called Install OS X El Capitan.app, is in its default location in your main Applications folder (/Applications).
- Select the text of the following Terminal command and copy it. Note that the window that displays the command scrolls to the right.
- Launch Terminal (in /Applications/Utilities).
- Warning: This step will erase the destination drive or partition, so make sure that it doesn’t contain any valuable data. Paste the copied command into Terminal and press Return.
- Type your admin-level account password when prompted, and then press Return.
- You may see the message “To continue we need to erase the disk at /Volumes/Untitled. If you wish to continue type (Y) then press return:” If so, type the letter Y and then press Return. If you don’t see this message, you’re already set.
The Terminal window displays createinstallmedia’s progress as a textual representation of a progress bar: Erasing Disk: 0%… 10 percent…20 percent… and so on. You also see a list of the program’s tasks as they occur: Copying installer files to disk…Copy complete.Making disk bootable…Copying boot files…Copy complete. The procedure can take as little as a couple minutes, or as long as 20 to 30 minutes, depending on how fast your Mac can copy data to the destination drive. Once you see Copy Complete. Done., as shown in the screenshot above, the process has finished.

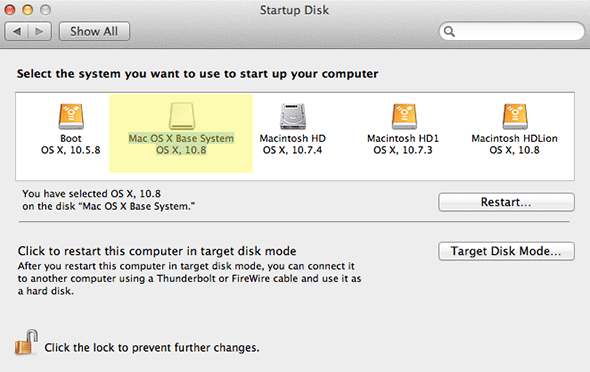
Createinstallmedia will have renamed your drive from Untitled to Install OS X El Capitan. You can rename the drive (in the Finder) if you like—renaming it won’t prevent it from working properly.
Booting from the installer drive
You can boot any El Capitan-compatible Mac from your new installer drive. First, connect the drive to your Mac. Then, restart your Mac (or, if it’s currently shut down, start it up) while holding down the Option key. When OS X’s Startup Manager appears, select the installer drive and then click the arrow below it to proceed with startup. (Alternatively, if your Mac is already booted into OS X, you may be able to choose the installer drive in the Startup Disk pane of System Preferences, and then click restart. However, sometimes OS X installer drives don’t appear in the Startup Disk window.)
Once booted from your installer drive, you can perform any of the tasks available from the OS X installer’s special recovery and restore features. In fact, you’ll see the same OS X Utilities screen you get when you boot into OS X Recovery—but unlike with recovery mode, your bootable installer includes the entire installer.
Contents
|
The general procedure to install Ubuntu (or Ubuntu flavour, Kubuntu, Lubuntu, Xubuntu, ...) from a USB flash drive is:
Get the correct Ubuntu installation file, 'the iso file', via this link or Ubuntu flavour via this link. Download the iso file into your running computer (for example into the directory Downloads in the internal drive, not into the USB flash drive that you want to make into a USB boot drive).
Check with md5sum (or another checksum tool) that the download was good.
- Put Ubuntu onto your USB flash drive alias 'stick' alias 'pendrive' alias 'thumb'. Tools for this purpose are described in this help page.
- Configure your computer to boot from USB flash drive and boot from it.
Try Ubuntu (Kubuntu, Lubuntu, Xubuntu, ...) before installing it.
- Install Ubuntu to your internal drive (hard disk drive or solid state drive or external drive).
See also: Installation/FromUSBStickQuick for beginners starting from Windows.
Ubuntu can be installed from a USB flash drive. This may be necessary for most new portable computers without DVD drives and is handy for others because a USB flash drive is so convenient. Also, you can configure Ubuntu on the USB flash drive to save changes you make, unlike a read-only CD/DVD disk.

Booting from a USB flash drive created with usb-creator alias Startup Disk Creator and mkusb will behave just as if you had booted from the install CD. It will show the language selection and then the install menu, from which you can install Ubuntu onto the computer's hard drive or launch the LiveCD environment. Other utilities, e.g. UNetbootin, may create slightly different boot drives or if on UEFI might not work at all with Debian iso files due to a bug
Note: This article uses the term 'USB flash drive' alongside USB stick, USB drive, USB device, USB pendrive and thumb drive.
To create a USB installation device, you will need:
a 4 GB USB flash device/drive/stick. If the iso file is smaller than 2 GB, it is possible to use a 2 GB USB device, at least with some of the methods. Files on this USB device will be erased, so backup the files you want to keep before making the device bootable. Some of the tools require that this USB device is properly formatted and mounted while other tools will overwrite whatever is on the target device. Please follow the instructions for each tool.
an Ubuntu flavour ISO file downloaded from an official web page, ubuntu.com/download or http://releases.ubuntu.com, stored in your running computer (for example in the directory Downloads in the internal drive, not in the USB flash drive that you want to make into a USB boot drive).
Check with md5sum (or another checksum tool) that the download was good. In Linux there is the tool 'md5sum'. In Windows you can do it with Rufus: click on the circle with a tick mark (more about Rufus here.)
Dummy headlines
After a major remake of this help page the following headlines are kept here because they may be linked to from other web sites. Several other headlines further down in the page are also kept for this reason.
Notes about speed
Notes about size
Notes about bootability
The flash hardware
There is a detailed description at the sub-page /pre |
There are various methods available for Windows to create a bootable Ubuntu USB flash drive.
NEVER try to use one of your hard disk drives or partitions in this process unless you really know what you are doing, as data will get erased.
Rufus
Rufus is the tool in Windows that is recommended officially by Ubuntu. A tutorial is available from here.
Download Rufus.

balenaEtcher
Download balenaEtcher
Pendrivelinux's Universal USB Installer
Download Universal USB Installer
UNetbootin
Download UNetbootin
Win32 Disk Imager
Download Win32 Disk Imager
There is a detailed description at /fromWindows including Rufus, balena Etcher, Universal USB Installer, Unetbootin and Win32 Disk Imager. |
Install and run Startup Disk Creator alias usb-creator
The Ubuntu Startup Disk Creator is dedicated to creating USB boot drives for Ubuntu and Ubuntu family flavours (Kubuntu, Lubuntu ... Xubuntu).
- Use another tool (e.g. 'UNetbootin' or 'mkusb'), if you want to create a USB boot drive with another Linux distro (alias Linux operating system).
You can find usb-creator-gtk by typing 'Startup Disk Creator' (Ubuntu Desktop) or usb-creator-kde in K-Menu-->Applications-->System-->Startup Disk Creator (Kubuntu). If it is not there, then you can install it using the Ubuntu Software Center.
- Insert and mount the USB drive. Inserting the USB drive should auto-mount it.
- Start the Startup Disk Creator
- In the top pane of the Startup Disk Creator, pick the .iso file that you downloaded.
- If the .iso file isn't listed, click 'Other' to locate and select the .iso file that you downloaded.
- In the bottom pane of the Startup Disk Creator, pick the target device, the USB flash drive. If more than one choice, please check carefully, until you are sure that you will be writing to the correct device.
- After checking that you are pointing to the correct target device, the USB flash drive, you can start the action.
You must enter a password because this is a risky operation. Use the password of the current user ID (the same as for login and running tasks with 'sudo'. Password is not required when installing from a 'live' system (booted from a DVD disk or another USB flash drive).
The Startup Disk Creator clones the iso file, which means that you need neither erase nor format the target drive. It will be completely overwritten anyway by the cloning process. The Startup Disk Creator looks like this in Ubuntu 18.04 LTS:
Screenshots: Startup Disk Creator - to SSD or pendrive
Notes
NEVER try to use one of your hard disk drives or SSDs or partitions in this process unless you really know what you are doing, as data will get erased.
There are bugs that affect the Ubuntu Startup Disk Creator, when you run it in old Ubuntu versions in BIOS mode and try to create USB boot drives with other versions. In the Ubuntu Startup Disk Creator version 0.3.2 in Ubuntu 16.04 LTS, these bugs are no longer a problem, so you can install any version of the Ubuntu flavours from 16.04 LTS and newer versions.
UNetbootin
Download UNetbootin
- UNetbootin works in and with most Linux distros.
- It is an extracting tool (not a cloning tool).
- It can make a persistence file up to 4GB in size to save data and defaults.
mkusb - dd image of iso file to USB device safely
Install mkusb via PPA
If you want to clone from a general image file to a drive, you can use mkusb. It lets you clone to any drive that is not busy, also an internal drive, and there are very obvious warnings to prevent mistakes.
- mkusb can also
- run in Debian and many linux distros that are similar to Ubuntu and Debian,
- clone from iso files of most Linux distros to create USB boot drives,
- create persistent live drives of the Ubuntu family and Debian, using all available drive space for persistence and/or data storage,
- restore a USB boot drive to a standard storage device.
There is a detailed description at /fromUbuntu including the Startup Disk Creator, UNetbootin and mkusb. |
See How to install Ubuntu on MacBook using USB flash drive and this Ubuntu Forum thread by Quackers
There is a good wiki page about booting with UEFI, and a good tutorial thread, UEFI Installing - Tips.
Test if running in UEFI mode
You may want to test if your Ubuntu flavour is running in [U]EFI mode. An installed system and a live system too is using the directory /sys/firmware/efi, so you can run the following command line,
The following command line is more robust and also easier to understand, so you may prefer it (if you copy & paste and are not bothered by typing a long command line),
Boot and install
Stable portable systems - good for USB sticks
Creating an EFI-only image
Ubuntu single boot in UEFI mode
'Do it yourself'
When the boot structure is modified in Ubuntu or the booting software, there can be problems until the extracting tools are modified to manage the modification. It is worthwhile to find a method that is as simple as possible and to learn how to use it in order to manage the extraction also when the boot structure is modified.
- For an UEFI only boot flash drive you need no installer
- Make the drive boot both in UEFI mode and BIOS mode
See this link: Installation/iso2usb#Do_it_yourself
Portable installed system booting from UEFI and BIOS
Multiboot pendrives
Booting ISO files on internal drive
Booting USB drives with grub2 and iso files 'grub-n-iso'
There are more details at the sub-page /alt |
Remove all unneeded USB items, but keep the network cable attached.
Boot menu
Instead of editing BIOS settings, you can choose a boot device from the boot menu. Press the function key to enter the boot menu when your computer is booting. Typically, the boot screen displays which key you need to press. It maybe one of F12, F10, F9.
Edit the BIOS settings
Insert the bootable USB flash drive that you just created in your target computer and restart it. Most newer computers can boot from a USB flash drive. If your computer does not automatically do so, you might need to edit the BIOS settings.
Restart your computer, and watch for a message telling you which key, hotkey to press to enter the BIOS setup.
- It will usually be one of F1, F2, F9, F10, DEL, Enter or ESC.
- The hotkey should be described in the user manual provided by the manufacturer of the computer (a printed or electronic document).
You can also search your hardware on boot-keys.org.
Press this hotkey continuously or tap repeatedly (different between computers) while your computer is booting to edit your BIOS settings. (On HP Mini Netbooks, the correct key is usually F9.)
Select 'hard disk/USB-HDD0'
Make Bootable Osx Usb
Note: with some motherboards you have to select 'hard disk/USB-HDD0' to choose the USB flash disk. It may work like this because the system sees the USB drive 'a mass storage device' as a hard disk drive, and it should be at the top of the boot order list.
So you need to edit the Boot Order. Depending on your computer, and how your USB key was formatted, you should see an entry for 'removable drive' or 'USB media'. Move this to the top of the list to make the computer attempt to boot from the USB device before booting from the hard disk.
Chainloading
PLoP Boot Manager
- For old computers that cannot boot from USB
Flow chart for trouble-shooting
See this link: Why Doesn't a Bootable USB Boot
There are problems with the versions of the Startup Disk Creator alias usb-creator in versions of Ubuntu older than 16.04 LTS. There are similar problems with old versions of Unetbootin. Until these problems are solved other tools work, for example mkusb and Win32DiskImager described in the following links, https://help.ubuntu.com/community/mkusb and https://wiki.ubuntu.com/Win32DiskImager/iso2usb
The version 0.3.2 (and newer versions) of the Startup Disk Creator alias usb-creator in Ubuntu 16.04 LTS (and newer versions) clones the iso file and creates a read-only file system. This method is very robust, but if you want to re-use the USB stick as a storage drive, you must restore it. Two methods are described in the next paragraph.
'Postrequisites' - after installation: how to restore the USB stick to a standard storage drive. The standard is an MSDOS partition table (MBR) and a partition with the FAT32 file system.
gparted
Make Bootable Osx Usb Without Mac
Disks
mkusb
There is a detailed description at the sub-page /post |
Make Bootable Usb Os X Catalina
FromUSBStickQuick for beginners starting from Windows
USB Installation Media: custom, manual, older versions, and technical instructions and troubleshooting. There are also network installation options available.
Why Doesn't a Bootable USB Boot: flowchart and lists of possible causes to help troubleshooting
MinimalCD alias mini.iso
booting with grub2
booting with UEFI
Ubuntu Forums tutorial 'Howto make USB boot drives'
Ubuntu Forums tutorial 'Howto help USB boot drives'
Ubuntu Forums tutorial 'How to create an external USB bootable Linux hard drive (without dual-boot)'
Unetbootin for Linux, Windows, Mac OS X
Paul Sutton's Unetbootin how to
Rufus - Create bootable USB drives the easy way (from Windows)
Pendrivelinux about Multisystem
Pendrivelinux about grub2
YUMI – Multiboot USB Creator
Choosing between Live USB and Full USB Installation
Try Ubuntu (Kubuntu, Lubuntu, Xubuntu, ...) before installing it
LiveCD/Persistence
Dual Boot with Windows
Discussion about tools to create USB boot drives at the Ubuntu Forums 'http://ubuntuforums.org/showthread.php?t=2291946'
Make Bootable Osx Usb Windows
CategoryLiveCategoryInstallationCategoryInstallationCategoryInstallation
